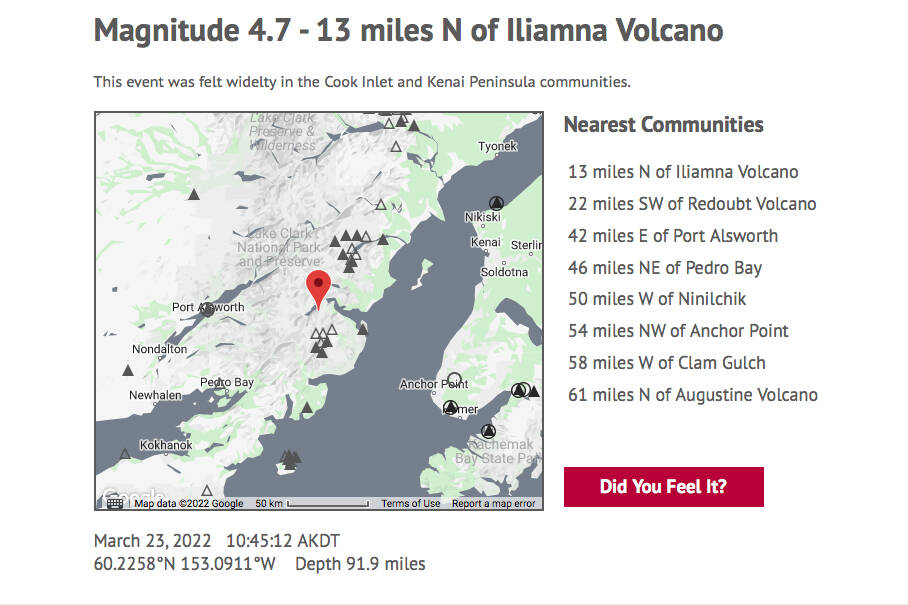
A 4.7 magnitude earthquake shook Kenai Peninsula communities at 10:45 a.m. Wednesday morning, according to the Alaska Earthquake Center.
The epicenter of the temblor struck just 13 miles north of Mount Iliamna, which is an active volcano on the west side of Cook Inlet.
A magnitude 5.1 earthquake struck the western side of Cook Inlet on March 12, centered 31 miles northwest of Kenai and 31 miles northeast of the Mount Redoubt volcano. A 3.6 magnitude earthquake struck 29 miles northeast of Kenai at a depth of 28 miles on March 8.
Wednesday’s tremor near Iliamna hit at a depth of 92 miles.
According to the earthquake center, strong quakes in southern Alaska are caused by the subducting Pacific and overriding North American tectonic plates. The second-largest rattle ever recorded worldwide struck under Prince William Sound in 1964. That earthquake was 9.2 on the Richter scale.
Some less devastating shakes are caused by the subducting Pacific Plate descending toward the mantle beneath the North American Plate. This zone of seismic activity extends from the Aleutian Arc to the Alaska Peninsula and Cool Inlet, where it ends underneath the northern foothills of the Alaska Range.
There were five other temblors on the Kenai Peninsula on Wednesday, as of 5 p.m.: a 1.9 magnitude in Clam Gulch, a 1.2 in Tyonek, a 1.1 in Nikiski, a 1.9 in Whittier and a 1.5 in Ninilchik.
Reach reporter Camille Botello at camille.botello@peninsulaclarion.com.