The weather is finally warm enough on the central Kenai Peninsula to sit outside in the evening without being wrapped in multiple layers. For many people, that means heading out to the deck.
And for many people, that deck may not be the safest place.
In 15 years of inspecting homes, Greg Swank has seen a lot of unsafe decks. When he’s taking a look at one, he typically kicks the railing— they’re supposed to hold 200 pounds — and checks the edges for rot. It’s more common than people expect, he said.
“Almost every deck has something wrong with it in some way that I look at,” he said.
Industry trade group the North American Deck and Railing Association estimates that about half the decks in the U.S. are past their useful life. The association has branded May as Deck Safety Month, in part because more people are getting out onto their decks for the summer.
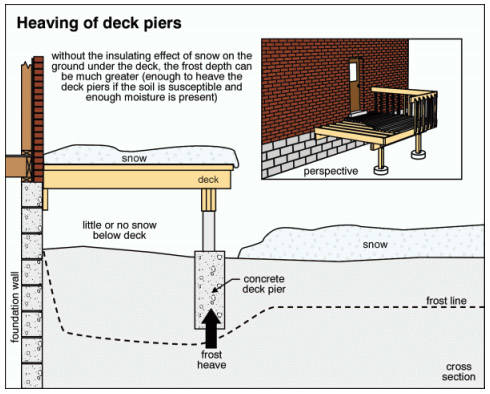
Swank, who owns Diligent Home Inspections, said he sees a lot of common mistakes in people’s decks, including improperly installed ledgerboards, heaving of deck piers or damage from snow buildup, among other problems. Most of the time, the issue is water getting into the wood and rotting the deck and possibly the wall of the house.
“There’s a lot that goes into it that you imagine a contractor would know,” he said. “But I imagine a lot of them weren’t built by contractors.”
In Alaska, one of the major issues is snow building up on the deck in the winter. When people don’t shovel it off, the freeze-thaw cycle can lead to water leaching between the boards of the deck and under a door, Swank said. That can damage the deck as well as the wall of the house. One way to avoid that is to either shovel it off or put down material to block water from getting under the door and threshold into the wall.
Improper nailing and fastening is a problem all over decks, leading to weakness in the structure, he said. Most deck collapses happen when a deck separates from the house and swings away. That can happen when a ledgerboard is only nailed to a house as opposed to proper lagging with flashing to prevent water getting behind it, he said.
When Swank is inspecting a deck, he carries a simple tool to check whether the wood is rotted — a screwdriver.
“I have tons of pictures where my screwdriver is completely buried in the wood (up to the handle),” he said. “Then you’ve got more than a flashing problem.”
Another common problem is joist hangers and fasteners. Swank said he often sees nails tonailed in — driven in at a 45-degree angle, which is likely to split the wood — rather than screwed in with a proper joist hanger. They can loosen over time but can be adjusted for safety.
Unsafe railings also cause issues, including being weak or too short, as are steps and handrails. Deck railings are required for any deck higher than 30 inches off the ground and are required to be at least three feet tall. They have to support 200 pounds, with spindles no more than 4 inches apart.
The most common problem Swank said he sees with steps is a poor connection between the stringer — the outer piece of wood — and the deck. Anything further 6 feet out from the deck requires a middle brace to hold the weight.
Home inspectors include a wide variety of items when they look at homes, from roofs to crawl spaces, and aren’t necessarily strictly for building code violations. Some things that don’t necessarily meet code may be safe over time, while others may be obvious problems, he said.
“I always tell people every inspection is like a treasure hunt,” he said. “You never know what you’re going to find.”
Reach Elizabeth Earl at eearl@peninsulaclarion.com.