As the executive branch of the federal government emphasizes the need for improved internet infrastructure highlighted by the pandemic, Alaska’s communication companies are looking at filling those gaps.
“Broadband is necessary for Americans to do their jobs, to stay connected equally for schools,” said Karine Jean-Pierre, White House deputy press secretary, in a media conference on Thursday. “Americans in rural areas and on tribal lands in particular lack broadband access.”
The pandemic, which saw schools and jobs go remote, made it “painfully clear” what the deleterious effect on students and workers with connectivity issues could be, Jean-Pierre said, especially for students who had connectivity issues. Those issues hit minority families especially hard, said Bharat Ramamurti, the deputy director of the National Economic Council for Consumer Protection, during the conference.
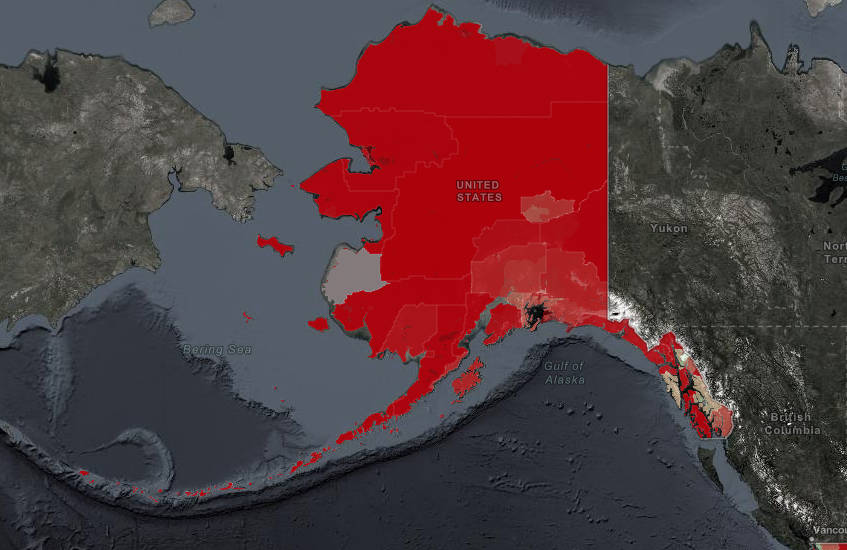
To that end, the National Telecommunications and Information Administration debuted a publicly accessible interactive map showing indicators for broadband need across the U.S.
On the map, Alaska is painted red, indicating broad swaths of primarily rural areas scoring poorly on metrics like speed tests and households without internet access. The Southeast is reasonably well connected, and Anchorage and Fairbanks are less grim, but for many of large census areas in Northern Alaska, as much as 53% of households in some regions don’t have internet access.
“As we release this important data to the public, it paints a sobering view of the challenges facing far too many Americans as they try to connect to high-speed broadband and participate in our modern economy,” said U.S. Secretary of Commerce Gina M. Raimondo in the news release. “In his American Jobs Plan, President Biden has proposed a once-in-a-lifetime investment that would finally connect one hundred percent of the country to reliable and affordable high-speed broadband.”
Close to home
In Alaska, companies, including Alaska Communications and GCI Communications Corp are looking at solutions to bring access to those located away from Alaska’s sparse urban centers.
“We have challenges delivering that kind of speed to more rural communities,” said Heather Handyside, vice president of corporate communications for GCI. “It’s because these are small communities surrounded by federally protected and regulated land.”
While GCI is able to provide reliable performance for urban centers and communities located along the highway system, as well as communities like Juneau, laying lines to smaller communities can get tied up in questions of regulation and permitting pertaining to tribal or federal lands, Handyside said. As well, laying fiber optic line isn’t cheap, coming in at approximately $75,000 and $100,000 per mile, Handyside said.
GCI also has hybrid fiber optic-microwave transmission networks, though these are less effective than the fiber optic networks or satellite service, Handyside said. GCI is working to expand its fiber optic lines, connecting faraway northern communities, while working on a $58 million project to expand service to communities in the Aleutians.
“When you connect Nome and Kotzebue with 1-gig speeds, you’ve effectively eliminated all broadband challenges to working from home,” Handyside said. “To live where your family is, to live where your culture is, that’s a benefit for all Alaska communities.”
ACS is also seeking to fill that gap in service for the rural clients, partnering with telecommunications company OneWeb to use low Earth orbit satellites to provide broadband service across the state, ACS recently announced.
“We see this as a milestone moment in our ability to offer low-latency, high-speed service across Alaska, particularly in rural areas,“ said Bill Bishop, president and CEO of Alaska Communications, in the news release.
GCI is considering satellites as an option, Handyside said, looking to find a good fit as technology improves and latency issues inherent in satellite communications drop. GCI is also looking to more than double the capability of its fiber optic lines in the next year, Handyside said.
A larger goal
As Alaskan companies work to bring access to far-flung corners of the state, the White House is looking at the larger prize as President Joe Biden seeks to get support for expanded broadband service as part of a larger infrastructure bill.
“The president has said that for $65 billion we can do three things,” Ramamurti said. “Provide and build that infrastructure for areas that don’t have it. Two, close the digital divide, which is that Black and Hispanic families tend to have access to broadband at much lower rates than other families. Three, lower costs. Families in the United States tend to pay for broadband at much higher rates than families in Europe and Asia.”
The $65 billion ask is part of a compromise with Republican lawmakers, down from an initial proposal for $100 billion for internet infrastructure.
“The bottom line for this map, in my view, is that need for investment in broadband infrastructure is huge,” Ramamurti said. “But the opportunities if we make that investment are huge also.”
• Contact reporter Michael S. Lockett at 757-621-1197 or mlockett@juneauempire.com.